
# Assume that sample porosity follows a normal distribution # You collect 12 rock core samples for each depth 5.4Non-parametric alternative: Bootstrapĭepth =.Pythonic Tip:Box-Cox transform with SciPy and Scikit-Learn.5.3Transform to normal distribution: Box-Cox.Notes:Be cautious with hypothesis testing for normality.
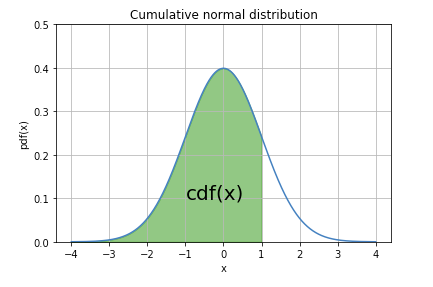 5.2Robustness of confidence intervals to non-normality. 5.1Problems of non-normal distributions and central tendency. 5Confidence interval of non-normal distribution. 4.4Confidence interval of other statistics: Bootstrap. Pythonic Tip:Computing confidence interval of variance with SciPy. Pythonic Tip:Computing paired t-interval. 4.2.3Dependent (paired) samples - Paired t-interval. Pythonic Tip:Computing Welch's t-interval. 4.2.2Independent (unpaired) samples, unequal variance - Welch's t-interval. Pythonic Tip:Computing student's t-interval. 4.2.1Independent (unpaired) samples, equal. Notes:Comparing means of more than two samples with ANOVA.
5.2Robustness of confidence intervals to non-normality. 5.1Problems of non-normal distributions and central tendency. 5Confidence interval of non-normal distribution. 4.4Confidence interval of other statistics: Bootstrap. Pythonic Tip:Computing confidence interval of variance with SciPy. Pythonic Tip:Computing paired t-interval. 4.2.3Dependent (paired) samples - Paired t-interval. Pythonic Tip:Computing Welch's t-interval. 4.2.2Independent (unpaired) samples, unequal variance - Welch's t-interval. Pythonic Tip:Computing student's t-interval. 4.2.1Independent (unpaired) samples, equal. Notes:Comparing means of more than two samples with ANOVA.  Pythonic Tip:Computing confidence interval of mean with SciPy. Notes:Distribution of various statistics. Pythonic Tip:Difference between Numpy variance. Notes:Population variance $\sigma^2$ vs. Example 3:Uncertainty in oil production forecast. Example 2:Purity of methamphetamine (crystal) in Breaking Bad. A confidence interval addresses this issue by providing a range of values, which is likely to contain the population parameter of interest within the range of uncertainty. How well a sample statistic estimates an underlying population parameter is always an issue ( Population vs. Due to the uncertainty involved with sample data, any statistical estimation needs to be delivered in a range, not in a point estimate. Sample data may not be a good representation of a population by numerous factors (Ex: bias), and as a result, uncertainty is always introduced in any estimations derived from sample data. Your best shot is to survey a small fraction ( samples) of the entire data set, and pray that your sample data represents the population reasonably well. It is difficult to obtain measurement data of an entire data set ( population) due to limited resource & time. For example: I am 95% confident that the population mean falls between 8.76 and 15.88 $\rightarrow$ (12.32 $\pm$ 3.56)Ĭonfidence interval tells you how confident you can be that the results from a poll or survey reflect what you would expect to find if it were possible to survey the entire population. In the other words, it is a range of values we are fairly sure our true value lies in.
Pythonic Tip:Computing confidence interval of mean with SciPy. Notes:Distribution of various statistics. Pythonic Tip:Difference between Numpy variance. Notes:Population variance $\sigma^2$ vs. Example 3:Uncertainty in oil production forecast. Example 2:Purity of methamphetamine (crystal) in Breaking Bad. A confidence interval addresses this issue by providing a range of values, which is likely to contain the population parameter of interest within the range of uncertainty. How well a sample statistic estimates an underlying population parameter is always an issue ( Population vs. Due to the uncertainty involved with sample data, any statistical estimation needs to be delivered in a range, not in a point estimate. Sample data may not be a good representation of a population by numerous factors (Ex: bias), and as a result, uncertainty is always introduced in any estimations derived from sample data. Your best shot is to survey a small fraction ( samples) of the entire data set, and pray that your sample data represents the population reasonably well. It is difficult to obtain measurement data of an entire data set ( population) due to limited resource & time. For example: I am 95% confident that the population mean falls between 8.76 and 15.88 $\rightarrow$ (12.32 $\pm$ 3.56)Ĭonfidence interval tells you how confident you can be that the results from a poll or survey reflect what you would expect to find if it were possible to survey the entire population. In the other words, it is a range of values we are fairly sure our true value lies in. 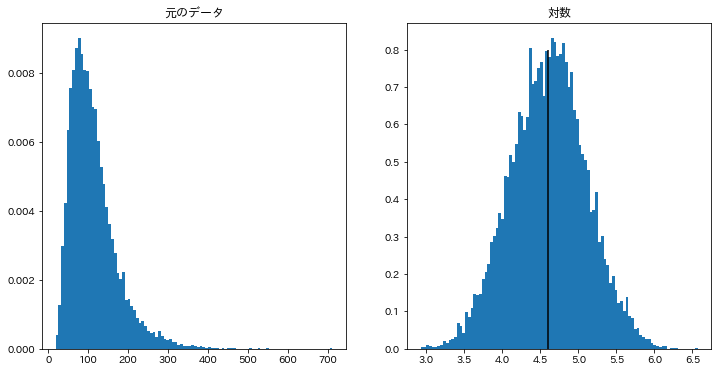
Confidence interval is uncertainty in summary statistic represented as a range.







 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
